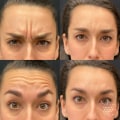
In the quest for radiant and youthful skin, chemical peels have emerged as a popular treatment option, offering remarkable results in skin rejuvenation. Among the various factors that contribute to the efficacy of these treatments, the have emerged as a popular treatment option, offering remarkable results in skin rejuvenation. Among the various factors that contribute to the efficacy of these treatments, the common acids used in peels play a pivotal role. Understanding these acids not only helps in making informed decisions regarding skincare but also demystifies the science behind achieving healthier skin. As we delve into the world of chemical peels, we uncover a rich palette of acids, each with its unique properties and benefits. From the gentle exfoliation offered by alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) to the deep-cleansing power of beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), these ingredients have been carefully selected for their ability to address various skin concerns.
Whether you're battling acne, pigmentation, or signs of aging, knowing which acids are commonly used can empower you to choose the right treatment tailored to your skin's needs. This article aims to explore the common acids used in peels, providing insights into their functions, benefits, and the types of peels they are typically found in. Join us as we navigate through this fascinating topic, equipping you with the knowledge to enhance your skincare routine and achieve the luminous complexion you desire.
Chemical peels
are a popular dermatological treatment designed to improve the appearance of the skin by removing its outermost layers. This process promotes skin rejuvenation and has gained significant traction in medical spas for various skin concerns such as acne, pigmentation, and signs of aging. Understanding the different types of acids used in these peels is crucial, as each acid has unique properties and benefits tailored to specific skin conditions. Chemical peels can be classified into three main categories: superficial peels, medium peels, and deep peels.Superficial peels, which utilize gentle acids, target only the outer layer of skin (epidermis) and are often used for minor issues like dry skin or mild discoloration. These peels require minimal recovery time and can be performed in a short office visit. Medium peels penetrate deeper into the skin (into the dermis) and are effective for more pronounced concerns such as moderate wrinkles or sun damage. Deep peels, on the other hand, reach the deeper layers of the skin and are reserved for severe issues like deep wrinkles or significant sun damage, often necessitating longer recovery times. One of the most common acids found in chemical peels is glycolic acidglycolic acid, derived from sugarcane.
As an alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), it works by loosening the bonds between dead skin cells, facilitating their removal, and revealing fresher skin underneath. Glycolic acid is particularly effective for treating acne, uneven skin tone, and fine lines. It is suitable for most skin types, especially oily and combination skin. Potential side effects may include mild redness or peeling, but these effects are typically short-lived.Salicylic acidSalicylic acid, a beta hydroxy acid (BHA), is another common ingredient used in chemical peels.
It is derived from willow bark and is known for its ability to penetrate oily skin and unclog pores. Salicylic acid is particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from acne, as it helps reduce inflammation and clear breakouts. Those with oily or acne-prone skin types may find this peel particularly advantageous. While generally well-tolerated, some users may experience dryness or irritation following treatment.
Lactic acid
is another AHA that comes from milk and is recognized for its gentle exfoliating properties.It not only helps with hyperpigmentation but also hydrates the skin due to its humectant properties. This makes lactic acid a great option for individuals with dry or sensitive skin who want to enhance their complexion without excessive irritation. Side effects can include mild redness or tingling, but these are usually temporary.
Trichloroacetic acid
(TCA) is often used in medium-depth peels. It is a versatile acid that can treat a range of skin issues, including fine lines, sun damage, and moderate scarring.TCA works by causing controlled damage to the skin, stimulating new collagen production as it heals. This type of peel is suitable for various skin types but should be approached with caution by those with darker complexions due to a higher risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Common side effects include peeling, redness, and sensitivity. Lastly, phenol peels represent one of the strongest forms of chemical peeling available. They penetrate deeply into the skin and are typically reserved for more severe cases of sun damage or deep wrinkles.
Phenol can produce significant results but requires longer recovery times than other types of peels. Due to its potency, it’s essential that candidates are carefully selected based on their skin type and history. Potential side effects include prolonged redness, swelling, and changes in pigmentation. While chemical peels can offer substantial improvements in skin texture and tone, there are many misconceptions surrounding them. One common myth is that chemical peels are painful; however, many patients report only mild discomfort during the procedure due to numbing agents applied beforehand.
Another misconception is that all chemical peels lead to significant downtime; while deeper peels do require more recovery time, many superficial treatments allow patients to return to daily activities almost immediately. It’s essential for readers considering chemical peels to consult with a qualified dermatologist or skincare professional who can provide personalized recommendations based on individual skin types and concerns. By understanding the various acids used in chemical peels and their specific benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their skincare treatments.
Salicylic Acid: The Acne Fighter
Salicylic acid is a powerful beta hydroxy acid (BHA) renowned for its effectiveness in treating acne. Its unique ability to penetrate deep into the pores sets it apart from other acids commonly used in chemical peels. When applied during a peel, salicylic acid works by dissolving the debris that clogs pores, such as excess oil and dead skin cells. This deep penetration allows salicylic acid to target the root causes of acne, effectively reducing inflammation and preventing future breakouts.Additionally, its exfoliating properties help to smooth the skin's texture, making it an ideal choice for individuals struggling with acne-prone skin. During a treatment, patients can expect a gentle application of salicylic acid, which may cause a slight tingling sensation. This is a normal response and indicates that the acid is working to clear the pores and promote healthier skin.
Glycolic Acid: The Powerhouse Exfoliant
Glycolic acid is a fruit acid derived from sugarcane, and it is renowned for its remarkable exfoliating properties. As one of the smallest alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), it penetrates the skin easily, making it highly effective in promoting cellular turnover. One of the primary benefits of glycolic acid is its ability to exfoliate the skin's surface gently. By sloughing off dead skin cells, it helps to reveal a fresher, more radiant complexion underneath.This process not only improves the texture of the skin but also enhances its overall appearance by reducing the visibility of fine lines and imperfections. Additionally, glycolic acid plays a significant role in brightening the skin. Its exfoliating action helps to fade dark spots and hyperpigmentation, resulting in a more even skin tone. Many individuals seeking to rejuvenate their skin find that regular treatments with glycolic acid lead to noticeable improvements in brightness and clarity. In summary, incorporating glycolic acid into chemical peels offers dual benefits: effective exfoliation and enhanced brightness. This powerhouse exfoliant is an excellent choice for those looking to achieve smoother, more luminous skin.
Lactic Acid: Gentle Yet Effective
Lactic acid is a popular choice in the realm of chemical peels, particularly due to its moisturizing properties and gentle nature.Derived from milk, this alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) is known for its ability to exfoliate the skin while simultaneously providing hydration, making it an ideal option for those with sensitive skin.One of the standout features of lactic acid is its capacity to enhance the skin's moisture levels. Unlike harsher acids that may strip the skin of its natural oils, lactic acid works by breaking down the bonds between dead skin cells, allowing for gentle exfoliation without causing irritation. This property makes it suitable for individuals who may have compromised skin barriers or are prone to redness and discomfort. Furthermore, lactic acid promotes a brighter complexion and can help fade dark spots over time. It not only improves skin texture but also supports overall skin health by encouraging cell turnover.
Patients seeking rejuvenation can expect a treatment that not only refreshes their appearance but also leaves their skin feeling soft and hydrated. In summary, lactic acid stands out in the world of chemical peels as a gentle yet effective option, particularly for those with sensitive skin seeking both exfoliation and moisture. Its unique properties allow for a nourishing treatment experience, ensuring that patients can enjoy the benefits of a peel without excessive irritation.
Phenol: The Deep Peel Option
Phenol is one of the most potent acids used in chemical peels, known for its ability to deliver significant skin rejuvenation results. This type of peel is often referred to as a deep peel due to its ability to penetrate deeply into the skin layers, targeting more severe skin issues such as deep wrinkles, significant sun damage, and precancerous growths. The use of phenol in chemical peels can result in dramatic improvements in skin texture and tone. However, due to its intensity, it is crucial to approach this treatment with caution.The procedure typically requires a longer recovery time compared to superficial or medium peels, and patients may experience swelling, redness, and peeling for several weeks post-treatment. Due to the strength of phenol, it is primarily recommended for individuals with specific skin concerns who are looking for substantial transformations. It is essential that patients are thoroughly evaluated by a qualified professional before undergoing a phenol peel, as improper use can lead to complications such as scarring or changes in skin pigmentation. In summary, while phenol offers remarkable results for deep skin rejuvenation, understanding its intensity and the necessary precautions is vital for ensuring a safe and effective treatment experience.
Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA): For Deeper Rejuvenation
Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA) is a powerful acid widely used in chemical peels, particularly for those seeking to address more significant skin issues. This acid penetrates deeper layers of the skin compared to milder acids, making it an effective option for various skin concerns such as scarring, hyperpigmentation, and fine lines. One of the primary benefits of using TCA in chemical peels is its ability to promote significant skin rejuvenation. It works by removing damaged skin layers, encouraging new skin growth and improving overall texture.Patients with acne scars or deep wrinkles often find TCA peels particularly beneficial, as these peels can help smooth out uneven skin surfaces. During a TCA peel treatment, patients may experience a sensation of tingling or burning as the acid is applied. This is typically followed by a period of redness and peeling as the skin begins to heal and regenerate. It is essential for individuals considering a TCA peel to consult with a qualified professional who can assess their skin type and determine the appropriate concentration of the acid for their specific needs. In summary, Trichloroacetic Acid is a potent option for deeper rejuvenation, particularly for those facing challenging skin issues. Its effectiveness makes it a popular choice in med spas for achieving smoother, more youthful-looking skin. In conclusion, understanding the common acids used in chemical peels is crucial for anyone considering these treatments for skin rejuvenation.
Each acid offers unique benefits tailored to different skin types and concerns, from the exfoliating prowess of glycolic acid to the targeted action of salicylic acid for acne. It is essential to choose the right type of chemical peel based on individual skin needs and goals. We encourage readers to consult with a qualified professional at a med spa to determine which peel is most suitable for their specific skin condition and desired outcomes. By being informed about these acids and their effects, individuals can make confident decisions about their skin care treatments and ultimately achieve healthier, revitalized skin.